使用的数据集为the Street View House Numbers(SVHN) dataset
为了建立一个半监督学习的情景,这里仅使用前1000个训练数据的标签,并且将GAN的判别器由二分类变为多分类,针对此数据,共分为11类(10个真实数字和虚假图像)
代码示例
代码的整体结构同前一篇博客生成对抗网络GAN介绍,这里仅注释有改动的部分
针对该网络更为细节的改进参考文章Improved Techniques for Training GANs以及对应的github仓库
- 数据处理
import pickle as pkl import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from scipy.io import loadmat import tensorflow as tf data_dir = 'data/' trainset = loadmat(data_dir + 'svhntrain_32x32.mat') testset = loadmat(data_dir + 'svhntest_32x32.mat') def scale(x, feature_range=(-1, 1)): x = ((x - x.min())/(255 - x.min())) min, max = feature_range x = x * (max - min) + min return x class Dataset: def __init__(self, train, test, val_frac=0.5, shuffle=True, scale_func=None): split_idx = int(len(test['y'])*(1 - val_frac)) self.test_x, self.valid_x = test['X'][:,:,:,:split_idx], test['X'][:,:,:,split_idx:] self.test_y, self.valid_y = test['y'][:split_idx], test['y'][split_idx:] self.train_x, self.train_y = train['X'], train['y'] ################### # For the purpose of semi-supervised learn, pretend that there are only 1000 labels # Use this mask to say which labels will allow to use self.label_mask = np.zeros_like(self.train_y) self.label_mask[0:1000] = 1 ################### self.train_x = np.rollaxis(self.train_x, 3) self.valid_x = np.rollaxis(self.valid_x, 3) self.test_x = np.rollaxis(self.test_x, 3) if scale_func is None: self.scaler = scale else: self.scaler = scale_func self.train_x = self.scaler(self.train_x) self.valid_x = self.scaler(self.valid_x) self.test_x = self.scaler(self.test_x) self.shuffle = shuffle def batches(self, batch_size, which_set="train"): ################### # Semi-supervised learn need both train data and validation(test) data # Semi-supervised learn need both images and labels ################### x_name = which_set + "_x" y_name = which_set + "_y" num_examples = len(getattr(self, y_name)) if self.shuffle: idx = np.arange(num_examples) np.random.shuffle(idx) setattr(self, x_name, getattr(self, x_name)[idx]) setattr(self, y_name, getattr(self, y_name)[idx]) if which_set == "train": self.label_mask = self.label_mask[idx] dataset_x = getattr(self, x_name) dataset_y = getattr(self, y_name) for ii in range(0, num_examples, batch_size): x = dataset_x[ii:ii+batch_size] y = dataset_y[ii:ii+batch_size] if which_set == "train": ################### # When use the data for training, need to include the label mask # Pretend don't have access to some of the labels yield x, y, self.label_mask[ii:ii+batch_size] ################### else: yield x, y dataset = Dataset(trainset, testset) - 搭建网络
### Input def model_inputs(real_dim, z_dim): inputs_real = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, *real_dim), name='input_real') inputs_z = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, z_dim), name='input_z') ################### # Add placeholders for labels and label masks y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, (None), name='y') label_mask = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, (None), name='label_mask') ################### return inputs_real, inputs_z, y, label_mask ### Generator def generator(z, output_dim, reuse=False, alpha=0.2, training=True, size_mult=128): with tf.variable_scope('generator', reuse=reuse): x1 = tf.layers.dense(z, 4 * 4 * size_mult * 4) x1 = tf.reshape(x1, (-1, 4, 4, size_mult * 4)) x1 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x1, training=training) x1 = tf.maximum(alpha * x1, x1) #(:,4,4,4*size_mult) x2 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(x1, size_mult * 2, 5, strides=2, padding='same') x2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x2, training=training) x2 = tf.maximum(alpha * x2, x2) #(:,8,8,2*size_mult) x3 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(x2, size_mult, 5, strides=2, padding='same') x3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x3, training=training) x3 = tf.maximum(alpha * x3, x3) #(:,16,16,size_mult) logits = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(x3, output_dim, 5, strides=2, padding='same') #(:,32,32,3) out = tf.tanh(logits) return out ### Discriminator ################### ### Add dropout layer to reduce overfitting since only 1000 labelled samples exist ### extra_class = 0: 10 class classification(10 digits) and set [fake logit=0] ### extra_class = 1: 11 class classification(10 digits+[fake image]) ### The two settings basically the same, but since the final purpose is classifying a real image to 10 digits, extra_class=0 may be more proper ################### def discriminator(x, reuse=False, training=True, alpha=0.2, drop_rate=0., num_classes=10, size_mult=64, extra_class=0): with tf.variable_scope('discriminator', reuse=reuse): # Add dropout layer x = tf.layers.dropout(x, rate=drop_rate/2.5) #Input layer (:,32,32,3) ################### x1 = tf.layers.conv2d(x, size_mult, 3, strides=2, padding='same') relu1 = tf.maximum(alpha * x1, x1) # Add dropout layer relu1 = tf.layers.dropout(relu1, rate=drop_rate) #(:,16,16,size_mult) ################### x2 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu1, size_mult, 3, strides=2, padding='same') bn2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x2, training=training) relu2 = tf.maximum(alpha * x2, x2) #(:,8,8,size_mult) ################### x3 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu2, size_mult, 3, strides=2, padding='same') bn3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x3, training=training) relu3 = tf.maximum(alpha * bn3, bn3) # Add dropout layer relu3 = tf.layers.dropout(relu3, rate=drop_rate) #(:,4,4,size_mult) ################### x4 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu3, 2 * size_mult, 3, strides=1, padding='same') bn4 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x4, training=training) relu4 = tf.maximum(alpha * bn4, bn4) #(:,4,4,2*size_mult) ################### x5 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu4, 2 * size_mult, 3, strides=1, padding='same') bn5 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x5, training=training) relu5 = tf.maximum(alpha * bn5, bn5) #(:,4,4,2*size_mult) ################### x6 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu5, 2 * size_mult, 3, strides=1, padding='valid') # This layer is used for the feature matching loss, don't use batch normalization on this layer # See the function model_loss for the feature matching loss relu6 = tf.maximum(alpha * x6, x6) #(:,2,2,2*size_mult) ################### # Flatten by global average pooling features = tf.reduce_mean(relu6, (1, 2)) #(:,2*size_mult) # Multi-classification class_logits = tf.layers.dense(features, num_classes + extra_class) #(:,10) or (:,11) out = tf.nn.softmax(class_logits) ################### # Split real and fake logits for classifying real and fake if extra_class==1: real_class_logits, fake_class_logits = tf.split(class_logits, [num_classes, 1], 1) #real(:,10); fake(:,1) fake_class_logits = tf.squeeze(fake_class_logits) #(number of samples,) else: real_class_logits = class_logits fake_class_logits = 0. # Set gan_logits such that P(input is real | input) = sigmoid(gan_logits) # For Numerical stability, use this trick: log sum_i exp a_i = m + log sum_i exp(a_i - m), m = max_i a_i mx = tf.reduce_max(real_class_logits, 1, keepdims=True) #(:,1) stable_real_class_logits = real_class_logits - mx #minus the largest real logit for each sample, (:,10) gan_logits = tf.log(tf.reduce_sum(tf.exp(stable_real_class_logits), 1)) + tf.squeeze(mx) - fake_class_logits #(number of samples,) ################### return out, class_logits, gan_logits, features ### Create GAN and Compute Model Loss def model_loss(input_real, input_z, output_dim, y, num_classes, label_mask, g_size_mult, d_size_mult, \ training=True, alpha=0.2, drop_rate=0.): g_model = generator(input_z, output_dim, alpha=alpha, size_mult=g_size_mult, training=training) d_on_real = discriminator(input_real, alpha=alpha, drop_rate=drop_rate, size_mult=d_size_mult, training=training) d_on_fake = discriminator(g_model, reuse=True, alpha=alpha, drop_rate=drop_rate, size_mult=d_size_mult, training=training) out_real, class_logits_real, gan_logits_real, features_real = d_on_real out_fake, class_logits_fake, gan_logits_fake, features_fake = d_on_fake ################### # Compute the loss for the discriminator # 1. The loss for the GAN problem, minimize the cross-entropy for the binary # real-vs-fake classification problem # 2. The loss for the SVHN digit classification problem, where minimize the # cross-entropy(use the labels) for the multi-class softmax d_loss_real = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=gan_logits_real, labels=tf.ones_like(gan_logits_real)) d_loss_real = tf.reduce_mean(d_loss_real) d_loss_fake = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=gan_logits_fake, labels=tf.zeros_like(gan_logits_fake)) d_loss_fake = tf.reduce_mean(d_loss_fake) y = tf.squeeze(y) #labels class_cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=class_logits_real, \ labels=tf.one_hot(y, class_logits_real.get_shape()[1], dtype=tf.float32)) # Use label_mask to ignore the examples pretending unlabeled for the semi-supervised problem class_cross_entropy = tf.squeeze(class_cross_entropy) label_mask = tf.squeeze(tf.to_float(label_mask)) d_loss_class = tf.reduce_sum(label_mask * class_cross_entropy) / tf.maximum(1., tf.reduce_sum(label_mask)) d_loss = d_loss_class + d_loss_real + d_loss_fake ################### # Compute the loss for the generator # Set the loss to the "feature matching" loss invented by Tim Salimans at OpenAI # This loss is the mean absolute difference between the real features and the fake features # This loss works better for semi-supervised learnings than the traditional generator loss real_moments = tf.reduce_mean(features_real, axis=0) fake_moments = tf.reduce_mean(features_fake, axis=0) g_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(real_moments - fake_moments)) ################### pred_class = tf.cast(tf.argmax(class_logits_real, 1), tf.int32) eq = tf.equal(y, pred_class) correct = tf.reduce_sum(tf.to_float(eq)) masked_correct = tf.reduce_sum(label_mask * tf.to_float(eq)) return d_loss, g_loss, correct, masked_correct, g_model ### Optimizer def model_opt(d_loss, g_loss, learning_rate, beta1): t_vars = tf.trainable_variables() d_vars = [var for var in t_vars if var.name.startswith('discriminator')] g_vars = [var for var in t_vars if var.name.startswith('generator')] with tf.control_dependencies(tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)): d_train_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate, beta1=beta1).minimize(d_loss, var_list=d_vars) g_train_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate, beta1=beta1).minimize(g_loss, var_list=g_vars) ################### # Decreasing learning rate shrink_lr = tf.assign(learning_rate, learning_rate * 0.9) ################### return d_train_opt, g_train_opt, shrink_lr ### Final GAN class GAN: def __init__(self, real_size, z_size, learning_rate, g_size_mult=32, d_size_mult=64, num_classes=10, alpha=0.2, beta1=0.5): tf.reset_default_graph() ################### # The dropout rate and the shrinking learn rate self.learning_rate = tf.Variable(learning_rate, trainable=False) self.drop_rate = tf.placeholder_with_default(.5, (), "drop_rate") ################### self.input_real, self.input_z, self.y, self.label_mask = model_inputs(real_size, z_size) self.training = tf.placeholder_with_default(True, (), "train_status") loss_results = model_loss(self.input_real, self.input_z, real_size[2], self.y, num_classes, self.label_mask, \ g_size_mult, d_size_mult, self.training, alpha, self.drop_rate) self.d_loss, self.g_loss, self.correct, self.masked_correct, self.samples = loss_results self.d_opt, self.g_opt, self.shrink_lr = model_opt(self.d_loss, self.g_loss, self.learning_rate, beta1) - 训练网络
def train(net, dataset, epochs, batch_size): saver = tf.train.Saver() sample_z = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=(50, z_size)) samples, train_accuracies, test_accuracies = [], [], [] steps = 0 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) for e in range(epochs): print("Epoch",e) num_examples = 0 num_correct = 0 for x, y, label_mask in dataset.batches(batch_size): steps += 1 num_examples += label_mask.sum() batch_z = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=(batch_size, z_size)) _, _, correct = sess.run([net.d_opt, net.g_opt, net.masked_correct], \ feed_dict={net.input_real: x, net.input_z: batch_z, net.y: y, net.label_mask: label_mask}) num_correct += correct ################### # At the end of the epoch: # Shrink the learning rate and compute train accuracy(only for labeled[masked] images) sess.run([net.shrink_lr]) train_accuracy = num_correct / float(num_examples) print("\t\tClassifier train accuracy: ", train_accuracy) ################### # At the end of the epoch: compute test accuracy num_examples = 0 num_correct = 0 for x, y in dataset.batches(batch_size, which_set="test"): num_examples += x.shape[0] correct = sess.run(net.correct, feed_dict={net.input_real: x, net.y: y, net.drop_rate: 0., net.training: False}) num_correct += correct test_accuracy = num_correct / float(num_examples) print("\t\tClassifier test accuracy", test_accuracy) ################### # Save history of accuracies to view after training train_accuracies.append(train_accuracy) test_accuracies.append(test_accuracy) ################### gen_samples = sess.run(net.samples, feed_dict={net.input_z: sample_z, net.training: False}) samples.append(gen_samples) saver.save(sess, './checkpoints/generator.ckpt') with open('samples.pkl', 'wb') as f: pkl.dump(samples, f) return train_accuracies, test_accuracies, samples - 最终结果并可视化
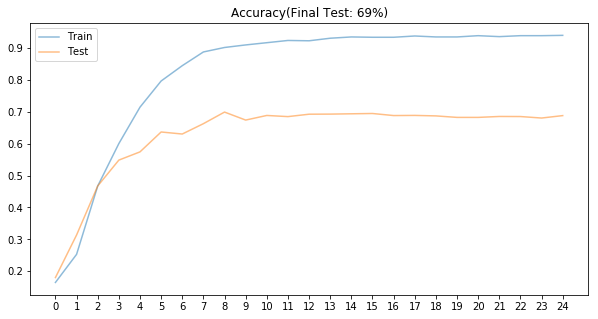
real_size = (32,32,3) z_size = 100 learning_rate = 0.0003 batch_size = 128 epochs = 25 net = GAN(real_size, z_size, learning_rate) train_accuracies, test_accuracies, samples = train(net, dataset, epochs, batch_size) ################### # Plot accuracies fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5)) plt.plot(train_accuracies, label='Train', alpha=0.5) plt.plot(test_accuracies, label='Test', alpha=0.5) ax.set_xticks(range(epochs)) plt.title("Accuracy(Final Test: {0}%)".format(int(round(test_accuracies[-1]*100)))) plt.legend()