本文使用Tensorflow实现字符到字符的预测(character-wise RNN)
训练文本使用的是《Anna Karenina》
建立的模型结构如下图所示
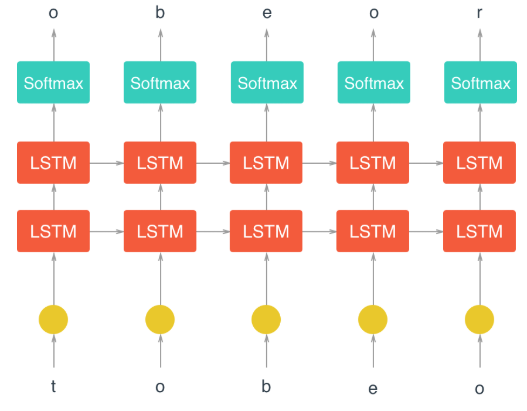
RNN建立和训练过程如下:
- 将文本中的字符编码为整数
import numpy as np with open('anna.txt', 'r') as f: text=f.read() vocab = sorted(set(text)) vocab_to_int = {c: i for i, c in enumerate(vocab)} int_to_vocab = dict(enumerate(vocab)) encoded = np.array([vocab_to_int[c] for c in text], dtype=np.int32) - 将编码后的文本转换成输入,每一个输入的batch为一个NxM的二维矩阵,其中N为batch size,M为sequence length(RNN处理的序列长度num_steps)
import tensorflow as tf def get_batches(arr, batch_size, num_steps): # Get the number of characters per batch and number of batches we can make chars_per_batch = batch_size * num_steps n_batches = len(arr)//chars_per_batch # Keep only enough characters to make full batches arr = arr[:n_batches * chars_per_batch].reshape((batch_size, -1)) for n in range(0, arr.shape[1], num_steps): # The features x = arr[:, n:n+num_steps] # The targets, shifted by one # For the very last batch, use zero to fill in the end of the targets y_temp = arr[:, n+1:n+num_steps+1] y = np.zeros(x.shape, dtype=x.dtype) y[:,:y_temp.shape[1]] = y_temp #iterator yield x, y - 建立RNN的输入层
def build_inputs(batch_size, num_steps): # Declare placeholders we'll feed into the graph inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, num_steps], name='inputs') targets = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, num_steps], name='targets') # Keep probability placeholder for dropout layers keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name='keep_prob') return inputs, targets, keep_prob - 建立RNN的隐藏层
### create a basic LSTM cell def build_cell(lstm_size, keep_prob): lstm = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(lstm_size) drop = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(lstm, output_keep_prob=keep_prob) #add dropout to the cell return drop ### Stack up multiple LSTM layers, for deep learning def build_lstm(lstm_size, num_layers, batch_size, keep_prob): cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([build_cell(lstm_size, keep_prob) for _ in range(num_layers)]) initial_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, tf.float32) return cell, initial_state - 建立RNN的输出层
def build_output(lstm_output, lstm_size): ###------------------------------------------------------------------------ ### Build a softmax layer, return the softmax output and logits. ### lstm_output: 3D tensor with shape (batch_size, num_steps, lstm_size) ### lstm_size: Size of the LSTM cells ###------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Reshape output so it's a bunch of rows # That is, the shape should be batch_size*num_steps rows by lstm_size columns x = tf.reshape(lstm_output, [-1, lstm_size]) # Connect the RNN outputs to a softmax layer with tf.variable_scope('softmax'): #avoid variable name conflict softmax_w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal((lstm_size, len(vocab)), stddev=0.1)) softmax_b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(len(vocab))) # Use softmax to get the probabilities for predicted characters logits = tf.matmul(x, softmax_w) + softmax_b out = tf.nn.softmax(logits, name='predictions') return out, logits - 构建损失函数和梯度下降优化
### build loss function def build_loss(logits, targets): # one-hot encode the targets,from 2D (batch_size, num_steps) to 3D (batch_size, num_steps, len(vocab)) y_one_hot = tf.one_hot(targets, len(vocab)) # reshape to match logits, one row per batch_size per num_steps y_reshaped = tf.reshape(y_one_hot, logits.get_shape()) # Softmax cross entropy loss loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=y_reshaped) loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss) return loss ### build optmizer for training, using gradient clipping to control exploding gradients def build_optimizer(loss, learning_rate, grad_clip): tvars = tf.trainable_variables() grads, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(tf.gradients(loss, tvars), grad_clip) train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate) optimizer = train_op.apply_gradients(zip(grads, tvars)) return optimizer - 建立RNN
class CharRNN: def __init__(self, batch_size=64, num_steps=50, lstm_size=128, \ num_layers=2, learning_rate=0.001, grad_clip=5, sampling=False): # When we're using this network for sampling later, we'll be passing in # one character at a time, so providing an option for that if sampling == True: batch_size, num_steps = 1, 1 else: batch_size, num_steps = batch_size, num_steps tf.reset_default_graph() # Build the input placeholder tensors self.inputs, self.targets, self.keep_prob = build_inputs(batch_size, num_steps) # Build the LSTM cell cell, self.initial_state = build_lstm(lstm_size, num_layers, batch_size, self.keep_prob) # One-hot encode the inputs, from 2D (batch_size, num_steps) to 3D (batch_size, num_steps, len(vocab)) x_one_hot = tf.one_hot(self.inputs, len(vocab)) # Run each sequence step through the RNN and collect the outputs outputs, state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, x_one_hot, initial_state=self.initial_state) self.final_state = state # Get softmax predictions and logits self.prediction, self.logits = build_output(outputs, lstm_size) # Loss and optimizer (with gradient clipping) self.loss = build_loss(self.logits, self.targets) self.optimizer = build_optimizer(self.loss, learning_rate, grad_clip) - 超参数设置
- num_layers一般设为2或3,lstm_size需根据数据量的大小确定
- 具体到该网络,要保证模型没有欠拟合,需要训练的参数个数最好和训练文本的总字符数在同一量级上(1MB的文件大约有100万个字符)
- 若训练过程中产生过拟合可以减小keep_prob或减小lstm_size
- 一个比较好的策略是在计算条件允许的情况下选择尽可能大的网络结构,同时尝试不同的dropout概率,选择使validation loss最小的那个
- 按照如下设置,该网络需训练的参数个数为(注:len(vocab)=83,训练文本的大小约为2MB)
batch_size = 100 num_steps = 100 lstm_size = 512 num_layers = 2 learning_rate = 0.001 keep_prob = 0.5 #Dropout keep probability ### Create RNN network model = CharRNN(batch_size=batch_size, num_steps=num_steps, lstm_size=lstm_size, num_layers=num_layers, learning_rate=learning_rate)
- 训练RNN
epochs = 20 # Print losses every N interations print_every_n = 50 # Save every N iterations save_every_n = 200 saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=100) ### train with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) counter = 0 for e in range(epochs): new_state = sess.run(model.initial_state) loss = 0 for x, y in get_batches(encoded, batch_size, num_steps): counter += 1 feed = {model.inputs: x, model.targets: y, \ model.keep_prob: keep_prob, model.initial_state: new_state} batch_loss, new_state, _ = sess.run([model.loss, model.final_state, model.optimizer], feed_dict=feed) if (counter % print_every_n == 0): print('Epoch: {}/{}... '.format(e+1, epochs), \ 'Training Step: {}... '.format(counter), \ 'Training loss: {:.4f}... '.format(batch_loss)) if (counter % save_every_n == 0): saver.save(sess, "checkpoints/i{}_l{}.ckpt".format(counter, lstm_size)) saver.save(sess, "checkpoints/i{}_l{}.ckpt".format(counter, lstm_size)) - 使用建立的RNN进行预测
### 从预测概率最高的n个字符中选取最终的预测字符 def pick_top_n(preds, vocab_size, top_n=5): p = np.squeeze(preds) #(1,1,vocab_size) to (vocab_size,) p[np.argsort(p)[:-top_n]] = 0 p = p / np.sum(p) c = np.random.choice(vocab_size, 1, p=p)[0] return c ### 预测字符 def sample(checkpoint, n_samples, lstm_size, prime="The "): samples = [c for c in prime] #the start characters model = CharRNN(lstm_size=lstm_size, sampling=True) saver = tf.train.Saver() with tf.Session() as sess: saver.restore(sess, checkpoint) new_state = sess.run(model.initial_state) x = np.zeros((1, 1)) for c in prime: x[0,0] = vocab_to_int[c] feed = {model.inputs: x, model.keep_prob: 1., model.initial_state: new_state} preds, new_state = sess.run([model.prediction, model.final_state], feed_dict=feed) c = pick_top_n(preds, len(vocab)) samples.append(int_to_vocab[c]) for i in range(n_samples-1): x[0,0] = c feed = {model.inputs: x, model.keep_prob: 1., model.initial_state: new_state} preds, new_state = sess.run([model.prediction, model.final_state], feed_dict=feed) c = pick_top_n(preds, len(vocab)) samples.append(int_to_vocab[c]) return ''.join(samples) ### 获得预测结果 checkpoint = tf.train.latest_checkpoint('checkpoints') samp = sample(checkpoint, 2000, lstm_size, prime="Far") #预测"Far"之后的2000个字符 print(samp)
